In this article, you will learn the python Keywords, built in Functions,String Methods,list Methods, Math Module, Random Module, Python Operators, and Python Dates, along with programming best practices.
What is python keywords?
It is a set of keywords that are reserved words that cannot be used as variable names, function names, or any other identifiers, like
|
Function
|
Description
|
|
class
|
To define a class
|
|
def
|
To define a function
|
|
In
|
To check if a value is present in a list, tuple, etc.True or false
|
|
True / Fulse
|
Boolean value, result of comparison operations
|
|
While
|
To create a while loop
|
|
pass
|
A null statement, a statement that will do nothing
|
|
import
|
To import a module
|
|
if
|
To make a conditional statement
|
|
else
|
Used in conditional statements
|
|
elif
|
Used in conditional statements, same as else if
|
What are the Built in Functions?
|
Function
|
Description
|
|
abs()
|
It returns the absolute value of a number
|
|
dir()
|
It returns list of the attributes and methods of any object
|
|
round()
|
It returns a floating point number that is a rounded version of the specified number, with the specified number of decimals
|
|
pow()
|
It returns the value of x to the power of y
|
|
max()
|
It returns the largest of the input values
|
|
min()
|
It returns the smallest of the input values
|
|
sum()
|
It calculates the total of all numerical values
|
|
len()
|
The number of elements stored in the object is never calculated, so len helps provide the number of elements
|
|
Format()
|
It formats the specified value(s) and insert them inside the string's placeholder
The placeholder is defined using curly brackets: {}
|
|
filter()
|
It filters the given sequence with the help of a function that tests each element in the sequence to be true or not
|
|
map()
|
It applies a given function to each item of an iterable (list, tuple etc.) and returns an iterator
|
|
reverse()
|
It reverses the elements of the list
|
|
super()
|
Returns an object that represents the parent class
|
Built in Functions: How to Call & write Functions?
What are the String Methods?
|
Function
|
Description
|
|
count()
|
It return the number of times the values appears int the list
|
|
find()
|
It used to return the lowest index value of the first occurrence of the substring from the input string; else it returns -1
|
|
rfind()
|
It finds the last occurrence of the specified value
|
|
split()
|
It split a string into a list where each word is a list item
|
|
join()
|
It join all items in a tuple / list into a string, using a hash character as separator
|
|
isalnum()
|
It returns True if all the characters are alphanumeric, meaning alphabet letter (a-z) and numbers (0-9)
|
|
isdigit()
|
It returns True if all the characters are digits, otherwise False
|
|
strip()
|
It remove spaces at the beginning and at the end of the string
|
|
lower()
|
It converts all uppercase characters in a string into lowercase characters and returns it
|
|
upper()
|
It converts all lowercase characters in a string into uppercase characters and returns it
|
|
swapcase()
|
It converts all uppercase characters to lowercase and all lowercase characters to uppercase characters of the given string, and returns it
|
|
title()
|
It returns a string where the first character in every word is upper case
|
String Methods: How to Call & write Functions?
Wha is list Methods?
|
Function
|
Description
|
|
sort()
|
It sorts the elements of a given list in a specific ascending or descending order
|
What are math module?
|
Function
|
Description
|
|
Remainder()
|
It returns the remainder when x is divided by y
|
|
sqrt()
|
It returns the square root of a number
|
What is Random module?
|
Function
|
Description
|
|
random()
|
It returns any random integer from 0 to 9
|
What are python Operators?
|
Operator
|
Description
|
|
*
|
Repeating strings
|
|
+
|
Add a variable to another variable
|
|
" "
|
To add a space
|
What does python Dates mean?
A date in Python is not a data type of its own, but we can import a module named datetime to work with dates as date objects.
Creating Date Objects
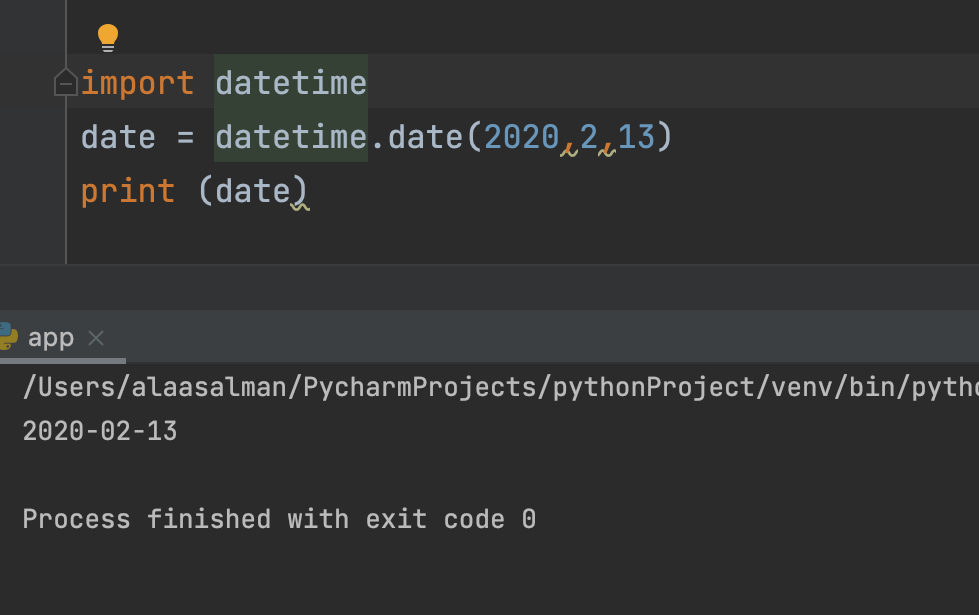
import datetime
Date = datetime.date(2020,2,13)
print (Date)
Current date
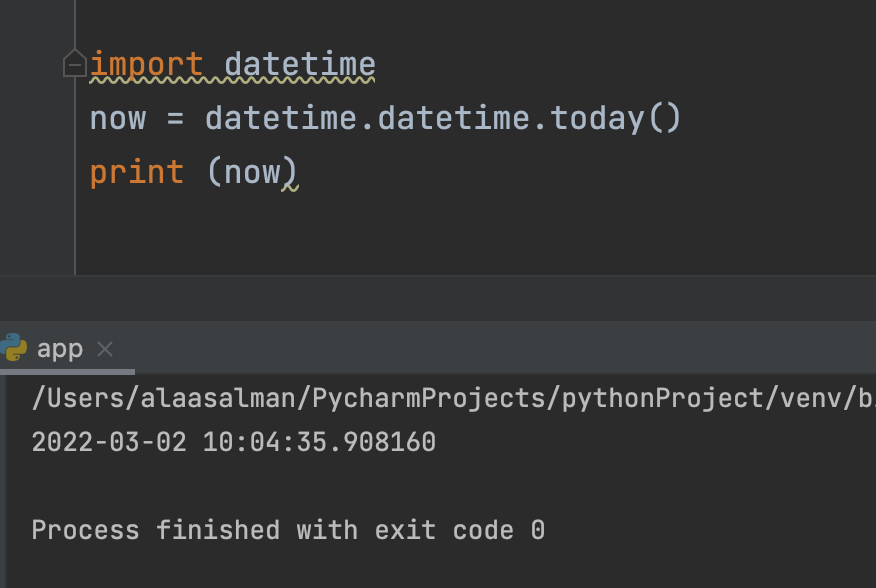
import datetime
now = datetime.datetime.today()
print (now)
python: How to call & write functions?
Conclusion
In this article, It has been discussed the Type of Functions,Python Operators, Python Dates.