In this post, we will list most of commoun Python methods that you should to know as a beginner
Python List Methods
- sort()
- Math Modules
- Random Modules
- Datetime
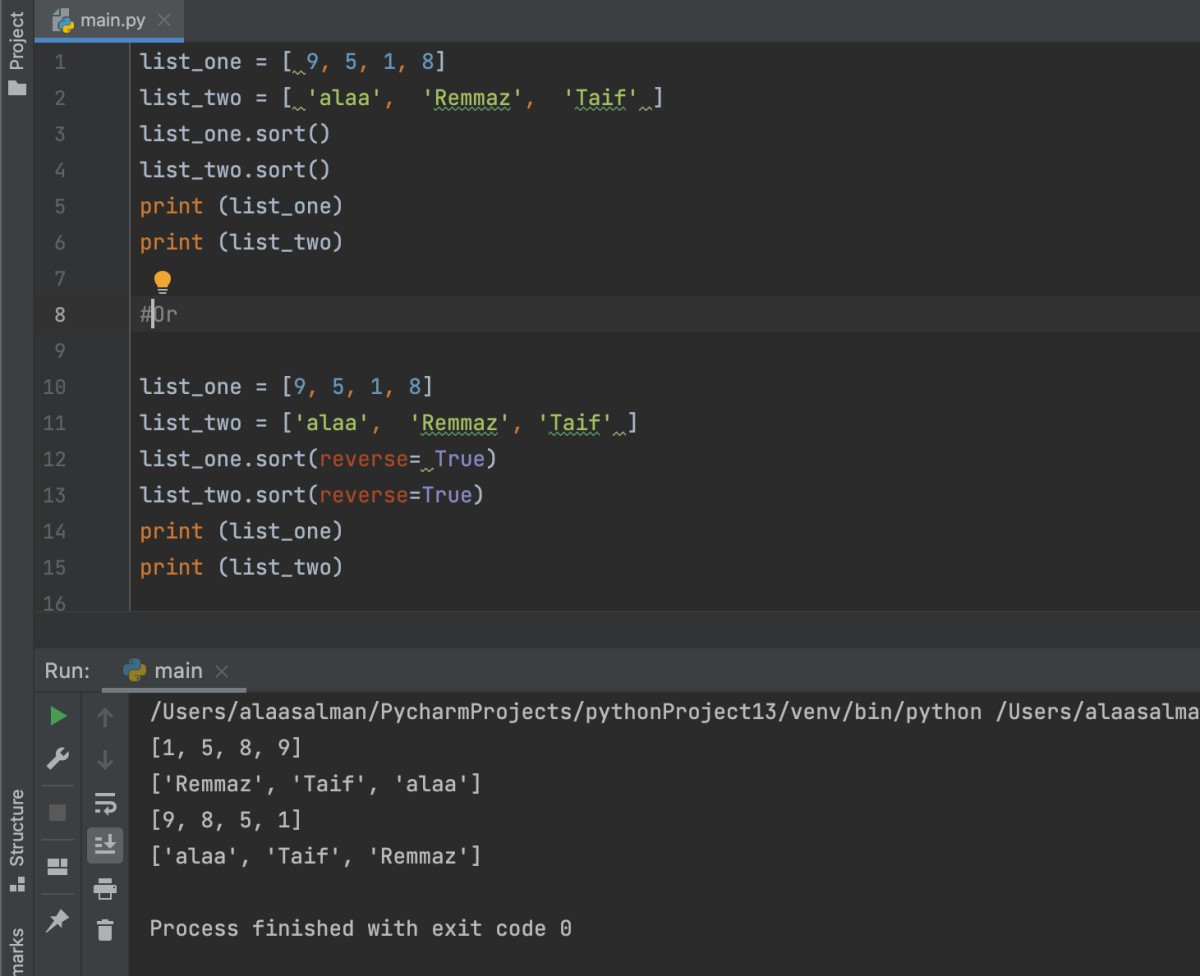
sort()
Math Module
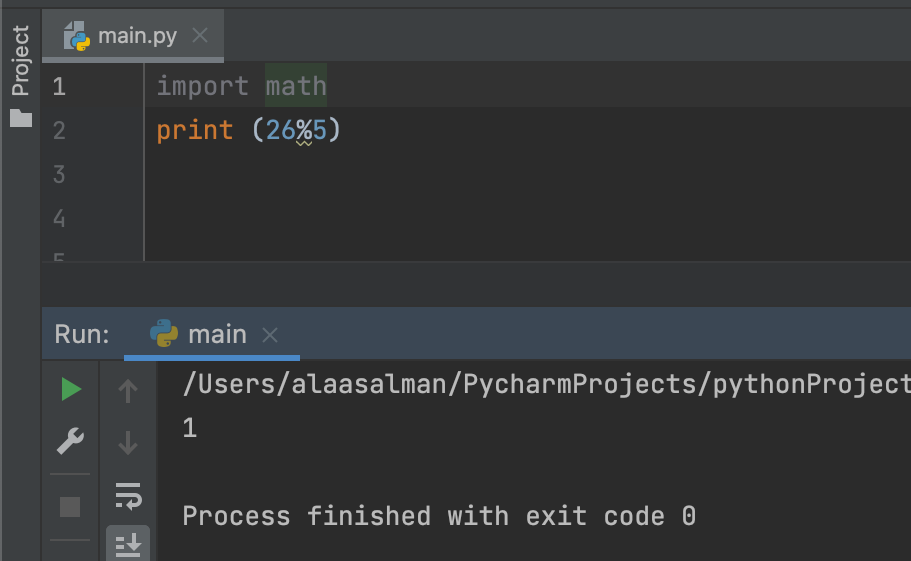
import math
print (26%5)
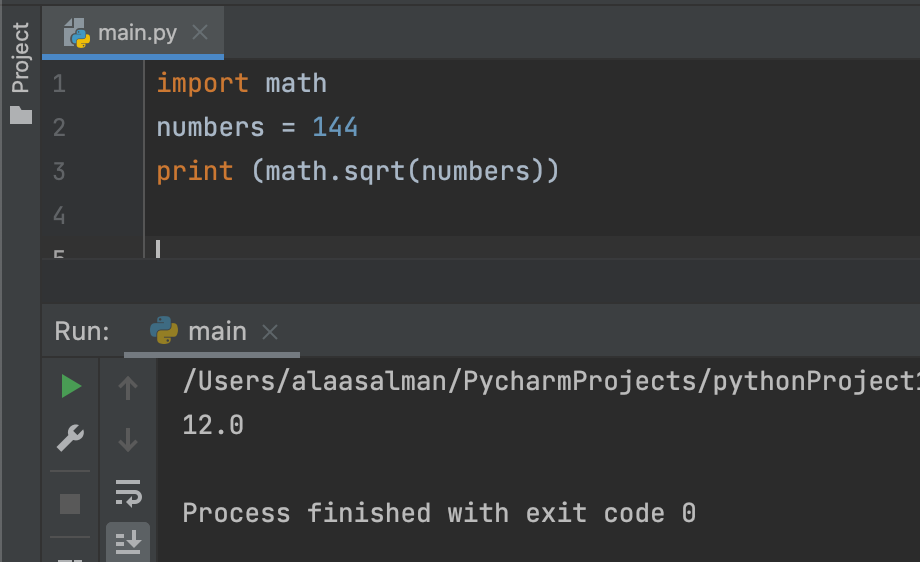
import math
numbers = 144
print (math.sqrt(numbers))
Random Module
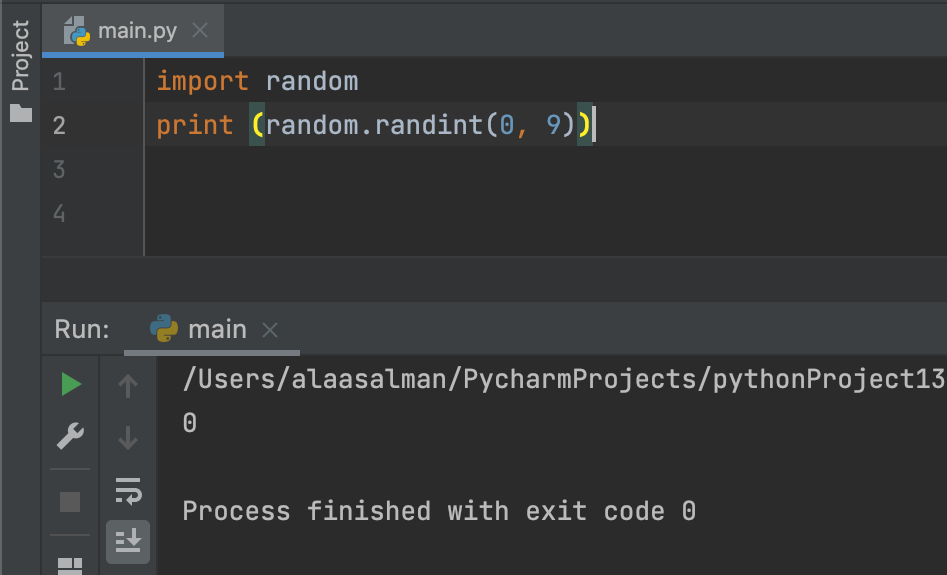
import random
print (random.randint(0, 9))
Python Operators
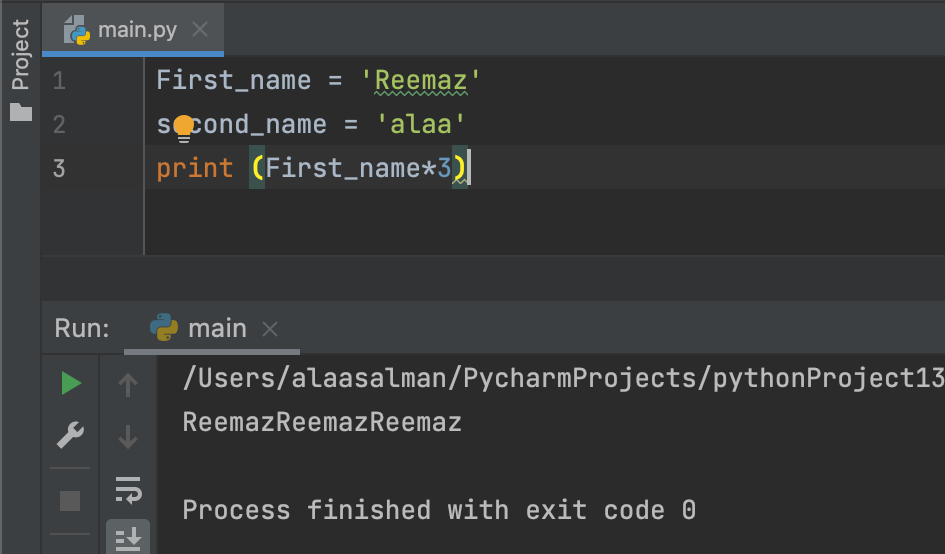
First_name = 'Reemaz'
second_name = 'alaa'
print (First_name*3)
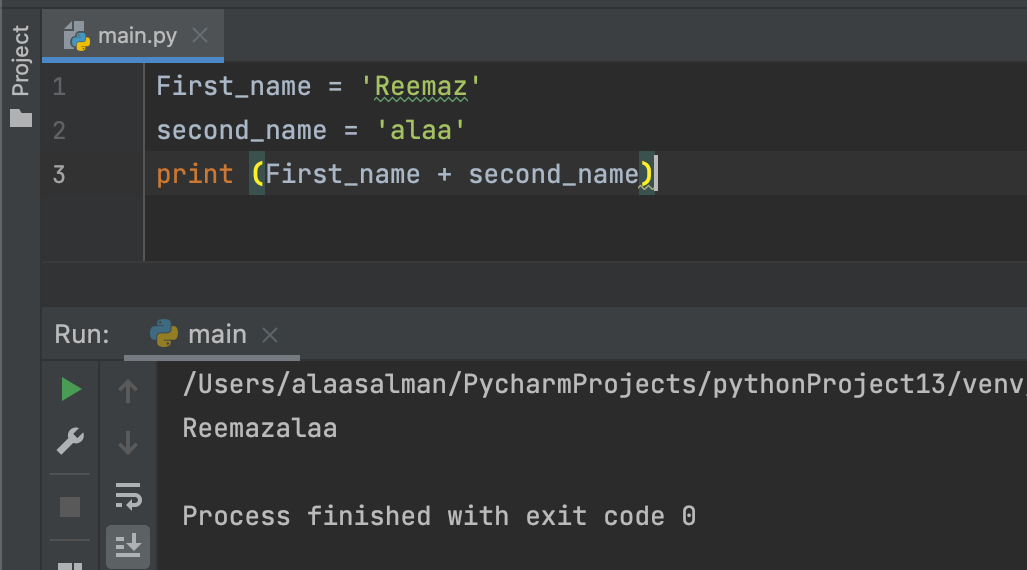
First_name = 'Reemaz'
second_name = 'alaa'
print (First_name + second_name)
Note: To add a space between them, add a " "
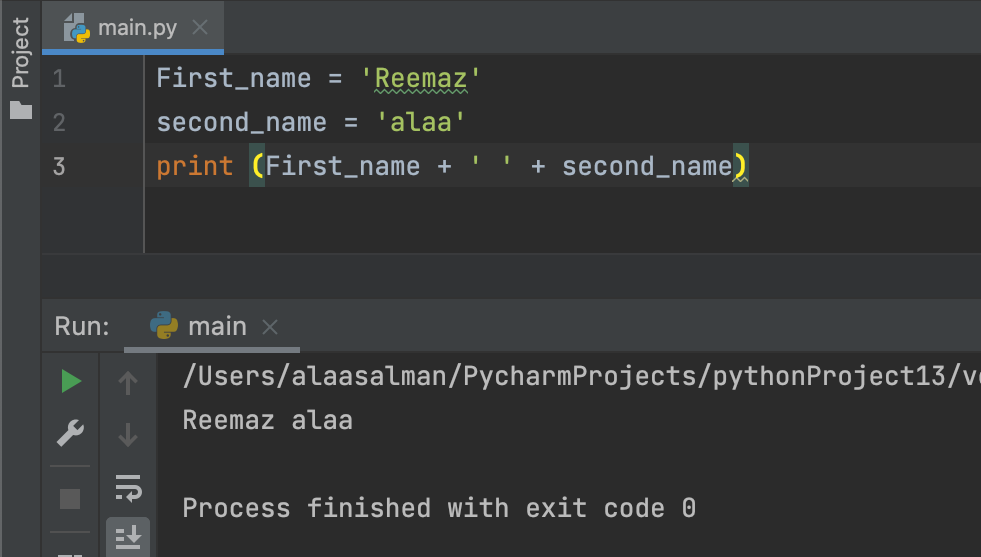
First_name = 'Reemaz'
second_name = 'alaa'
print (First_name + ' ' + second_name)
-
datetime to string using strftime()
The table below shows all the codes that you can pass to the strftime() method.
|
Directive
|
Meaning
|
Example
|
|
%a
|
Abbreviated weekday name.
|
Sun, Mon, ...
|
|
%A
|
Full weekday name
|
Sunday, Monday, ...
|
|
%w
|
Weekday as a decimal number.
|
0, 1, …, 6
|
|
%d
|
Day of the month as a zero-padded decimal.
|
01, 02, ..., 31
|
|
%j
|
Day of the year as a decimal number.
|
001, 002, ..., 366
|
|
%b
|
Abbreviated month name.
|
Jan, Feb, ..., Dec
|
|
%B
|
Full month name.
|
January, February, ...
|
|
%M
|
Minute as a zero-padded decimal number.
|
00, 01, ..., 59
|
|
%m
|
Month as a zero-padded decimal number.
|
00, 01, ..., 59
|
|
%Y
|
Year with century as a decimal number.
|
2013, 2019 etc.
|
|
%y
|
Year without century as a zero-padded decimal number.
|
00, 01, ..., 99
|
|
%H
|
Hour (24-hour clock) as a zero-padded decimal number.
|
00, 01, ..., 23
|
|
%I
|
Hour (12-hour clock) as a zero-padded decimal number.
|
01, 02, ..., 12
|
|
%p
|
Locale’s AM or PM.
|
AM, PM
|
|
%S
|
Second as a zero-padded decimal number.
|
00, 01, ..., 59
|
|
%f
|
Microsecond as a decimal number, zero-padded on the left.
|
000000 - 999999
|
For Example
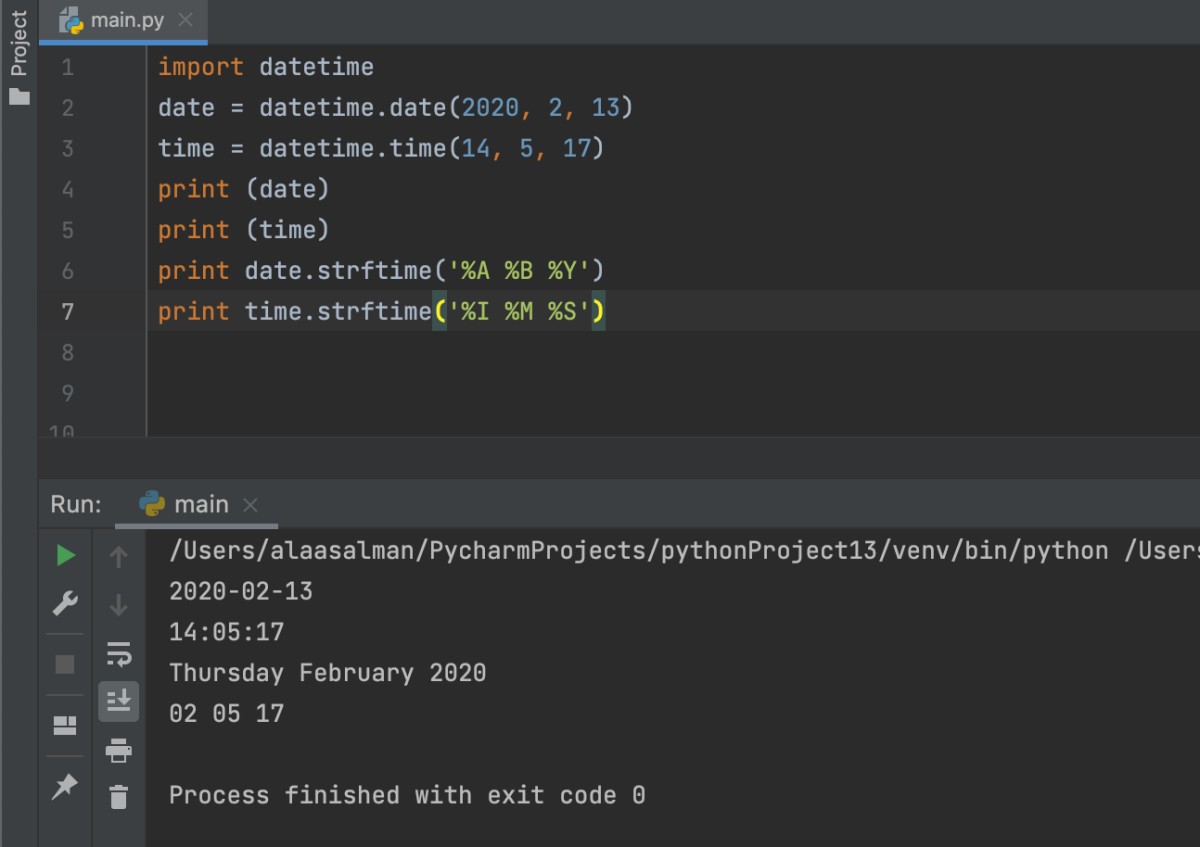
import datetime
date = datetime.date(2020, 2, 13)
time = datetime.time(14, 5, 17)
print (date)
print (time)
print date.strftime('%A %B %Y')
print time.strftime('%I %M %S’)
Functional programming In Python